
However, glandular fever can cause tiredness and loss of energy for up to a few months. What is the prognosis for glandular fever?
post-viral fatigue, where you feel low and tired. Mono throat skin#
a mild inflammation of your liver causing yellowing of your skin (mild jaundice). a widespread red (not itchy) rash and other skin conditions. a neurological illness, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome or Bell's palsy. a lower level of blood cells, such as anaemia. damaged spleen – this is rare and is usually a result of contact sport. However, there can be complications. These include: Most people with glandular fever will have few, if any, long-term complications other than fatigue. Are there any complications with glandular fever? Getting enough rest and sleep is important but complete bed rest is not recommended as it can make the symptoms of fatigue last longer. You may need to reduce some of your normal activities for a while. gradually increasing activity levels as you are able to.Īs glandular fever is caused by a virus, antibiotics won't be effective. avoiding strenuous activities and exercise. drinking lots of fluids, especially water. medicines for pain and fever, eg, paracetamol or ibuprofen. Treatment focuses on reducing symptoms until recovery and includes: There is no specific medical treatment for glandular fever. In some situations, blood tests may be required to help confirm the diagnosis. In many cases, your doctor will be able to make a diagnosis based on your history and examination. If you have a sore throat and fever that has lasted for more than a few days, you should see your doctor or nurse for advice. If you do get symptoms, you can be infectious for up to 7 weeks beforehand, and for many months after your symptoms go away. Only some people who are exposed to the virus get the symptoms of glandular fever. This can happen by touching hands, or sharing toys, eating utensils and drink bottles or by kissing. However, these viruses can also spread through blood and semen during sexual contact, blood transfusions and organ transplantations. It is spread mainly by close contact with saliva (spit) or nasal (nose) secretions of infected people. Many people in the community have the Epstein-Barr virus. Occasionally, the symptoms of glandular fever can last for 6 months or more. Not everyone infected with the virus gets symptoms and many people have had glandular fever at some time without knowing. Most people get better in 2–4 weeks, but some people may feel tired for several more weeks. Swelling around your eyes – about 1 in 5 people with glandular fever become quite puffy and swollen around the eyes. However, the glands in your neck are usually the most prominent. 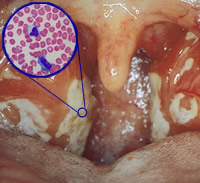
Any lymph gland in your body can be affected. Swollen glands around your neck – as your body's immune system fights off the virus it causes your lymph glands to swell.Flu-like symptoms – like other viral infections, glandular fever often causes a high temperature (fever), muscle aches and headaches.

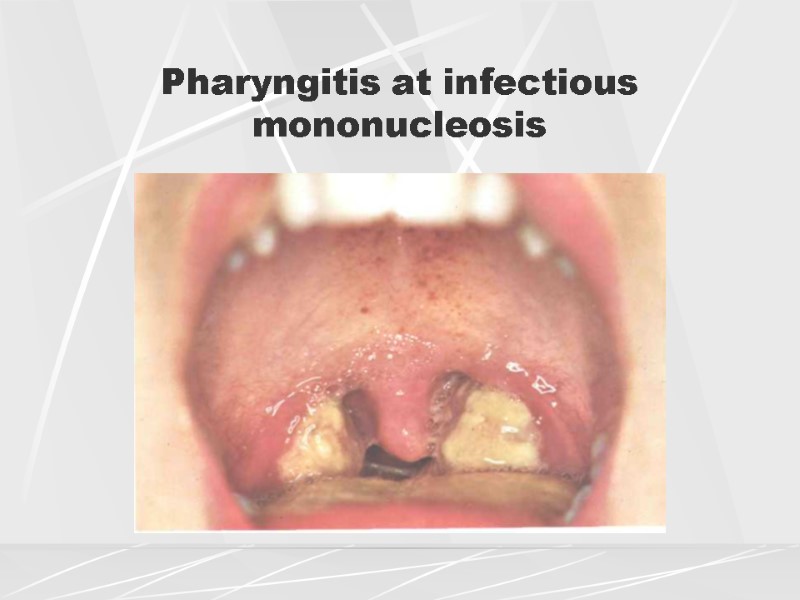
Swallowing is often painful and saliva may pool in your mouth. Glandular fever is typically suspected when tonsillitis is severe and lasts longer than usual.
Sore throat – although this may be mild, your throat is usually very sore, red and swollen. Tiredness – a feeling of intense tiredness often develops with glandular fever. Symptoms may develop slowly and may not all occur at the same time. Usually symptoms of glandular fever appear 4–6 weeks after you get infected with the Epstein-Barr virus. What are the symptoms of glandular fever? See your doctor if you have the symptoms because if it's not treated, there can be complications. Not everyone infected with the virus gets symptoms and many people have had glandular fever at some time without knowing. Most people get better in 2–4 weeks, but you may feel tired for several months. Symptoms can include fever, sore throat, sore glands and tiredness. It spreads mainly through saliva, which is why it is sometimes called the 'kissing disease'. Glandular fever is most often caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Glandular fever is a common infectious condition most often seen in teenagers and young adults.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
